We are entering the second full week of April 2020 and what is projected to be the peak incidence of deaths from COVID19 in the United States. What contributes to a severe or critical COVID19 infection? Do complex chronic illnesses such as Lyme disease or mold illness increase the risk of contracting COVID19 or increase the severity of the infection? Read on to learn more.
We are not out of the woods yet. We could see the same number of deaths from COVID-19 from this point forward as we have already seen. The projection is based on people continuing to practice the behaviors that have been successful in reducing the number of cases like social distancing and wearing face masks. If people begin to lighten up on their safety diligence because we have reached the peak incidence, we may see COVID19 linger longer than expected.
How Does the COVID19 Virus Cause Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)?
The most concerning symptom associated with COVID19 is respiratory distress. In certain individuals, the viral infection can progress rapidly and cause acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) – and possibly death.
Why do a majority of people who contract the SARS-CoV-2 virus (the virus that causes COVID19) recover while a small percentage become critically ill and require hospitalization or even die? The outcome of the infection is dependent on the infected person’s immune response to the virus. In severe cases, the rapid elevated inflammatory response is called the cytokine storm. People with a history of chronic infections such as Lyme disease are familiar with cytokine storms and referred to as a “Herx” reaction (short for Jarisch-Herxheimer).
In COVID19, the SARS-CoV-2 virus enters the lung and makes its way to the terminal branches of the lung called the alveoli. In normal circumstances, the alveoli are the structure where oxygen from the lungs is exchanged with carbon dioxide from the blood. However, in COVID19, the virus replicates once inside cells of the lung causing tissue damage.
The immune system responds to the virus and recruits more immune cells – including cytokines – that create inflammation. Inflamed lung tissue has an increase in permeability, leading to fluid buildup in the alveoli preventing oxygen exchange with the blood. Blood no longer delivers oxygen to the rest of the body, so organs and tissue become starved of oxygen. This is when ventilation comes in and hopefully prevents death.
Here is an excellent video illustration of this process.
Does Lyme Disease and Mold Illness Increase the Risk of COVID19?
Many of my patients want to know if their pre-existing chronic illness puts them at an increased risk for contracting COVID19. If they become infected, are they more susceptible to developing a complicated or critical case of COVID-19?
The immune system status may give us insight as to whether or not someone is at an increased risk for contracting COVID19. Blood tests such as white blood cell counts, immunoglobulin levels, and natural killer cell activity from Quest labs are useful measures to assess a person’s immune health. Subjectively, whether or not someone gets sick frequently, gets chronic sore throats or sinus infections, or swollen lymph nodes are also clues into the health of a person’s immune system.
Most people who develop severe cases of COVID19 requiring hospitalization and possibly ventilation seem to have a level of immune dysregulation before contracting the virus. The cytokine storm that causes the pathology associated with COVID19 determines the severity of the disease. When the immune system is properly regulated, people that become infected with COVID19 will have a moderate inflammatory response. Many people with complex chronic illnesses already take natural compounds that regulate the immune system, so they may have a reduced risk of developing a severe cytokine storm.
Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS) and COVID-19
Mast cells are immune cells that are located in areas of the body that interface with the outside world, such as the respiratory tract. Given that the SARS-CoV-2 virus binds to cells in the lungs, it is no surprise mast cells can be activated in COVID19. When triggered, mast cells release chemical mediators such as histamine and cytokines that contribute to a variety of physiological responses, including inflammation and increased permeability of tissues.
Therapies that stabilize mast cells to reduce the release of their contents and treatments that block histamine receptors (antihistamines) to prevent histamine’s effect on tissue are an essential part of an effective treatment plan for COVID19. Quercetin – a natural bioflavonoid that stabilizes mast cells – has been shown to inhibit influenza virus infections that have caused other seasonal epidemics and pandemics.
The Cytokine IL-6 in COVID-19
The cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) has been associated with the severity of COVID19. A meta-analysis of multiple studies demonstrated IL-6 levels are 2.9 fold higher in patients with complicated COVID19 compared to people with uncomplicated COVID19. A study using the IL-6 blocking drug tocilizumab confirmed improved outcomes in patients with COVID19. Now the drug manufacturer Roche has launched a controlled investigation using tocilizumab to treat severe cases of COVID19.
Turmeric Reduces IL-6
Turmeric has been studied for its cytokine reducing properties, specifically its ability to reduce IL-6 levels and IL-6 signaling in multiple research studies. I frequently prescribe turmeric for my patients because of its many benefits, including reducing inflammation. A review article summarizes several studies describing the cytokine lowering benefits of turmeric. Another meta-analysis of nine randomized controlled trials concluded curcumin (the active compound in turmeric) significantly reduced IL-6 levels.
Turmeric is it is poorly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Higher quality turmeric and turmeric that is formulated with other ingredients for better absorbability work the best. In my practice, my patients report the formula Cytoquel by Researched Nutritionals is quite effective at reducing inflammation and cytokines.
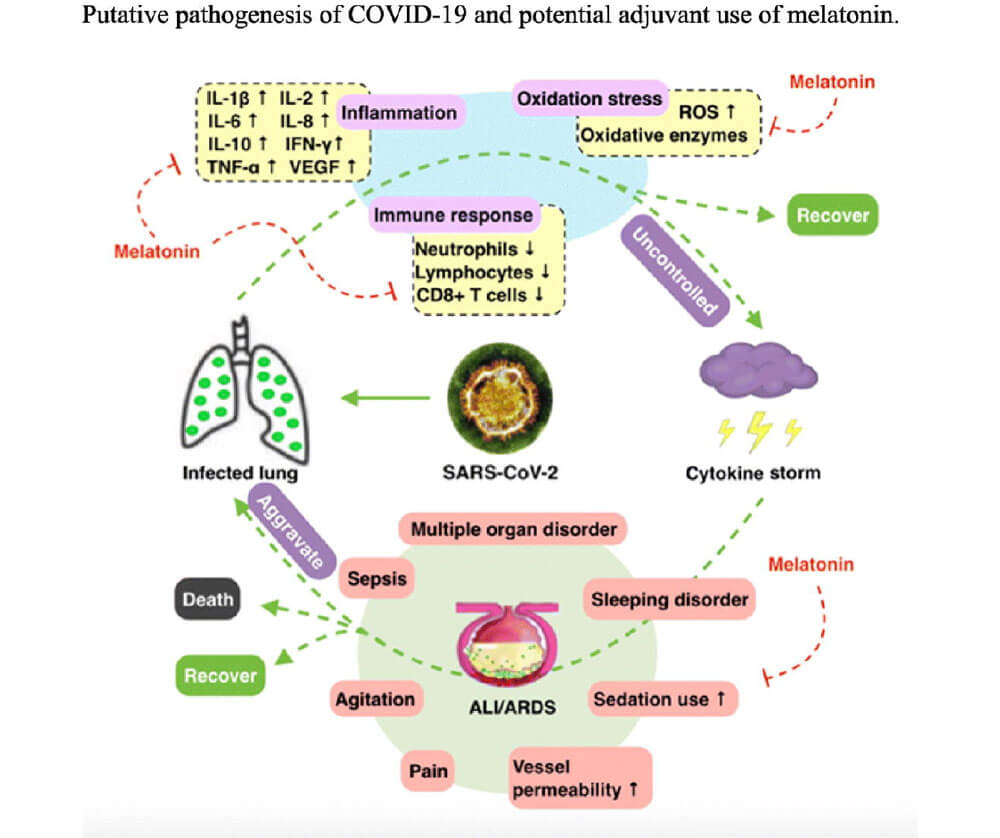
Inflammasome NLRP3 Inhibited by Melatonin
Part of the immune response in a lung infection is called the NLRP3 inflammasome. NLRP3 inflammasome elevates during acute lung injury, like the tissue damage from viral replication and the subsequent immune response in COVID19. The hormone melatonin has both anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative properties and also decreases viral load in infections.
Melatonin production declines as we age, and lower levels may be associated with increased critical cases and death in the elderly. Theoretically, this may be the reason children and adolescents are not developing severe illness from COVID19 is due to higher levels of melatonin.
Multiple published research studies describe the beneficial effects melatonin has on the NLRP3 inflammasome. The authors of the article COVID-19: Melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment, provide a thorough overview of the potential benefits of melatonin in the treatment of COVID19. Another study supports the use of melatonin to reduce NLRP3 inflammasome in sepsis.
What Can You Do to Protect Yourself From COVID19?
We are reaching a critical point of the COVID19 pandemic in the United States. Some states recently reached the peak incidence of deaths, while others will be reaching theirs in the next week or two. We need to continue our diligence following the guidelines to continue to reduce the number of cases and deaths related to COVID19.
The difference between mild and severe cases (and deaths) from COVID19 is related to the severity of inflammation and the cytokine response in the lungs. The risk for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is reduced by taking proven natural compounds such as turmeric, quercetin, and melatonin. Many drugs being studied or considered for the treatment of COVID19 are expensive and come with adverse side effects.
People with complex chronic illnesses such as Lyme disease, mold illness, or mast cell activation syndrome do not have an increased risk of contracting COVID19 but might have a predisposition to a heightened inflammatory response. There are several natural compounds that are effective at inhibiting the inflammatory cytokines that lead to the severity of disease progression in COVID19.