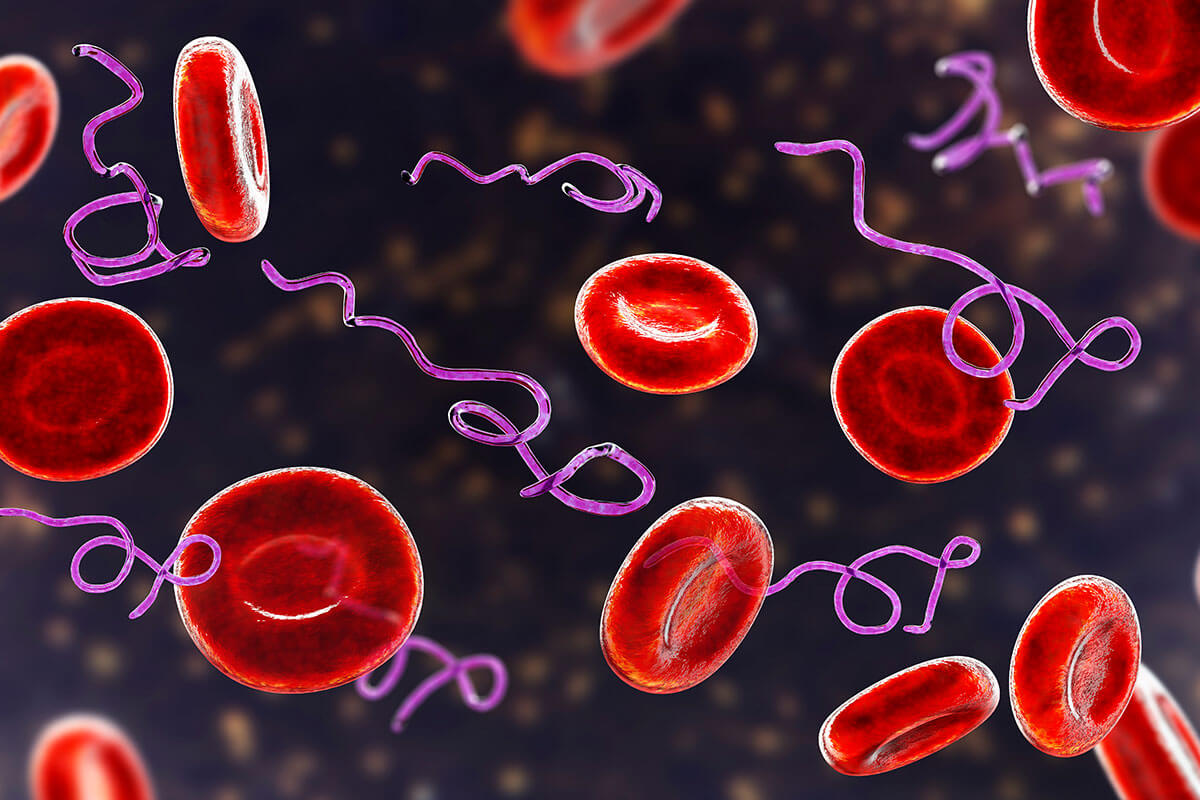
The bacteria that cause Lyme disease and associated infections can spread to any tissue or organ in the body causing a multi-system, multi-symptom presentation. In addition, the immune response to these bacteria creates a symphony of inflammation throughout the body leading to tissue damage and symptoms. Lyme disease symptoms can manifest in part of the body making it difficult to diagnose.
Read below to learn more about Lyme disease symptoms.
Hormones in Lyme Disease
Chronic infections, including Lyme disease, can affect every organ system in the body, including the endocrine system. When the body is under assault from a chronic infection, organ system function is compromised, contributing to insufficient levels of thyroid, adrenal, and sex hormones. Inadequate production or release of hormones produced by these glands causes the same…
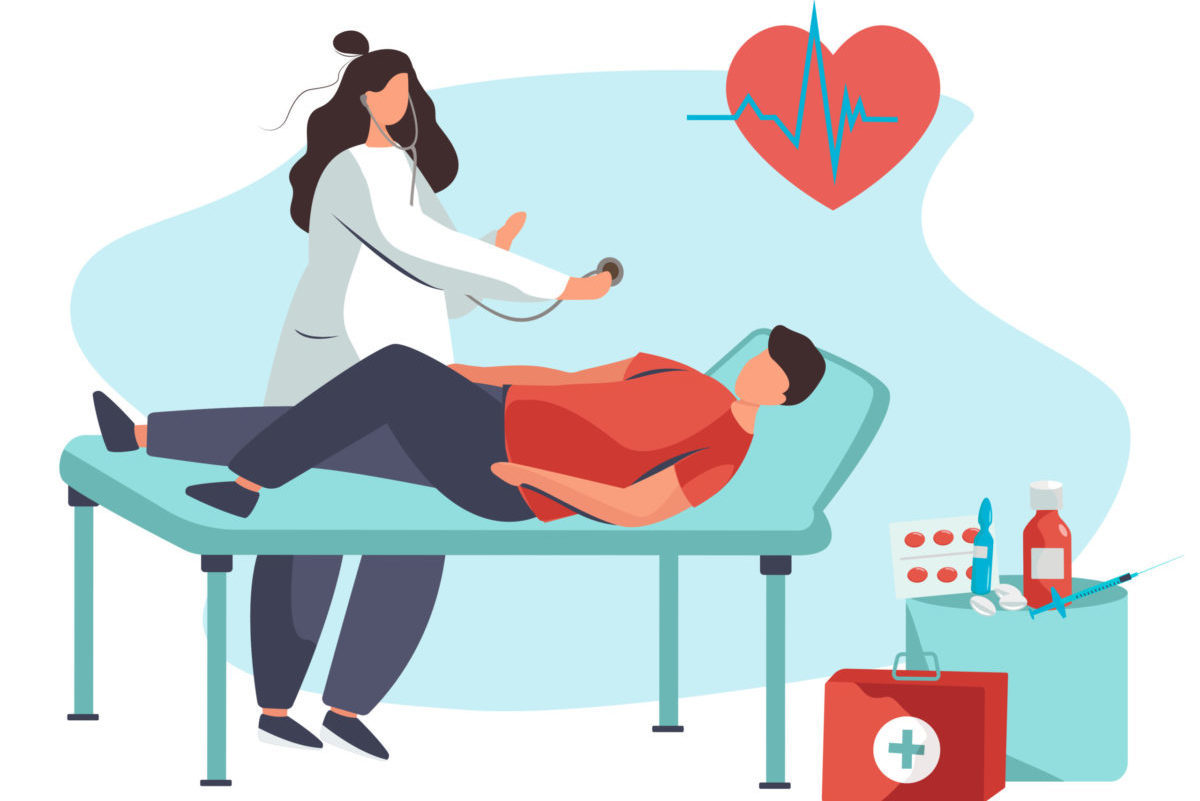
What is Lyme Carditis?
Following a tick bite, the bacteria that cause Lyme disease (Borrelia) can spread to various organs and tissues in the body. When the heart becomes infected with Borrelia, the disease state is called Lyme carditis. Between 4%-10% of people with untreated Lyme disease develop Lyme carditis, but only 1% of people with known Lyme disease…
Symptoms of Lyme Disease
Symptoms of Lyme disease can vary from person to person and typically manifest in multiple systems in the body. Neuropsychiatric symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and brain fog are quite common in Lyme disease. In 2020, Lyme-literate psychiatrist Robert Bransfield, MD, and his team published their findings of Lyme disease’s most common symptoms. The paper,…
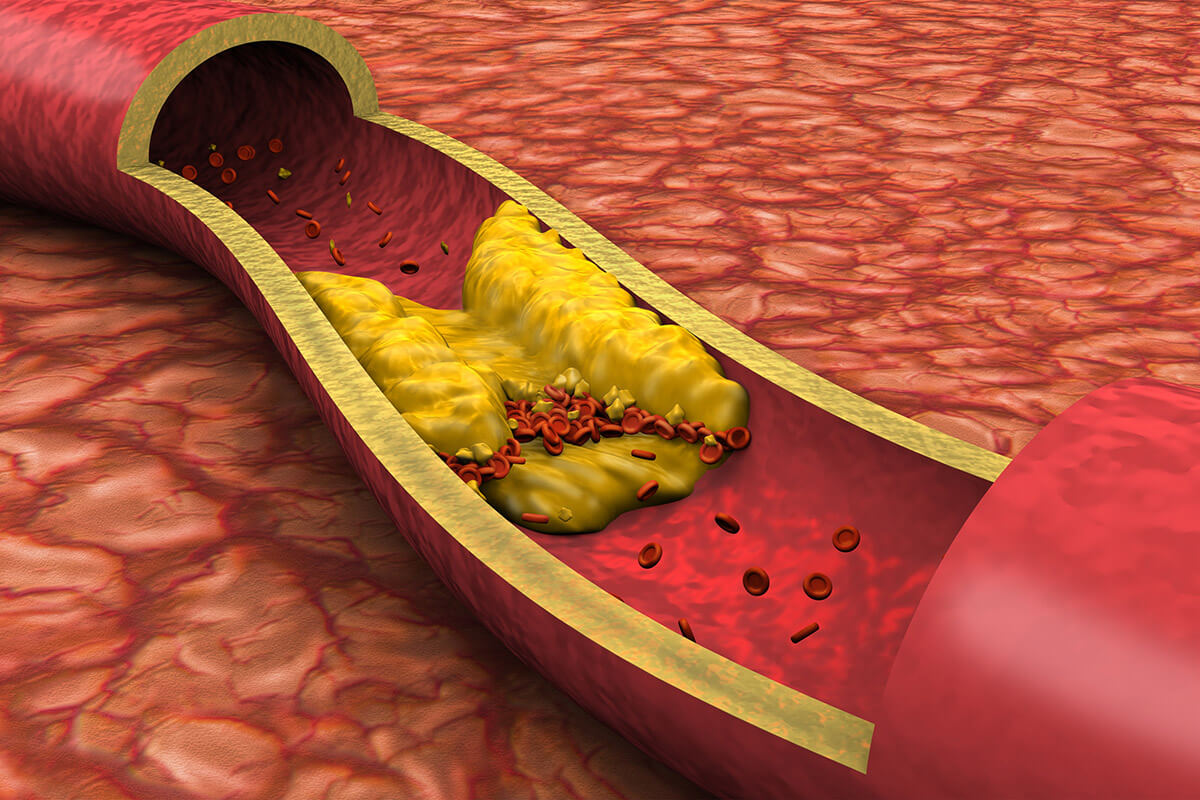
Hypercoagulation in Lyme Disease
The human body has more than 60,000 miles of blood vessels. These arteries and blood vessels are much more than just plumbing for blood. Arteries deliver oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and growth factors to cells. Veins remove toxins and waste products of metabolism from cells. The immune system also circulates in the bloodstream to protect us from…
Lyme Disease and Depression
Mood disorders and mental illness are common manifestations of Lyme disease and other tick-borne infections. In acute Lyme disease, cognitive impairment (what most refer to as brain fog) is a common symptom. However, when tick-borne infections go undiagnosed for a long period of time, people can experience a range of neuropsychiatric symptoms. Lyme disease can…
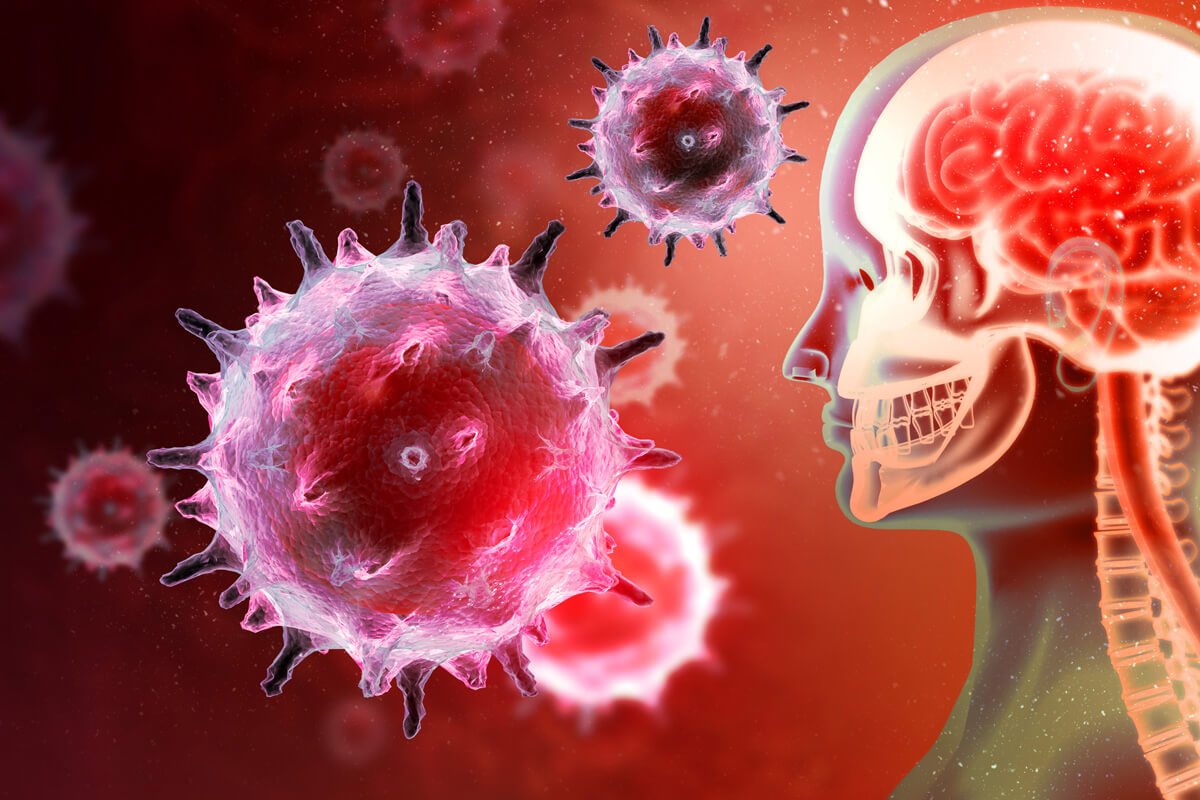
Neurological Lyme Disease
The bacteria that cause Lyme disease and its associated infections can affect the central, peripheral and autonomic nervous systems. Lyme neuroborreliosis refers to central nervous system dysfunction caused by Lyme disease. In an early infection with Lyme disease, the bacteria can penetrate the central nervous system leading to symptoms such as facial palsy, headaches, nausea/vomiting,…
Lyme Disease Fatigue
Fatigue is one of the most common and debilitating symptoms associated with Lyme disease and associated infections. The fatigue can either be persistent and low-grade or can be cyclical with other symptoms related to the infections. Some suffering with fatigue from Lyme disease, they have to manage how much energy they can expend in a…
Pain and Arthritis in Lyme Disease
Pain and arthritis are two of the most common symptoms of Lyme disease. Lyme disease was discovered in 1975 because of an outbreak of pain and arthritis in children and adults in Lyme, CT. After calls to the CDC by concerned parents, rheumatologist Alan Steere was sent to Lyme to investigate this bizarre cluster of…
Gastrointestinal Symptoms of Lyme Disease
The spirochete that causes Lyme disease – Borrelia burgdorferi – and the associated tickborne infections such as Bartonella and Babesia can directly affect any organ system in the body, including the gastrointestinal tract. About 80% of the immune system is located around the digestive tract, so digestive health influences the immune response. Gastrointestinal symptoms of…